How to Create a Reverse Charge Invoice Template
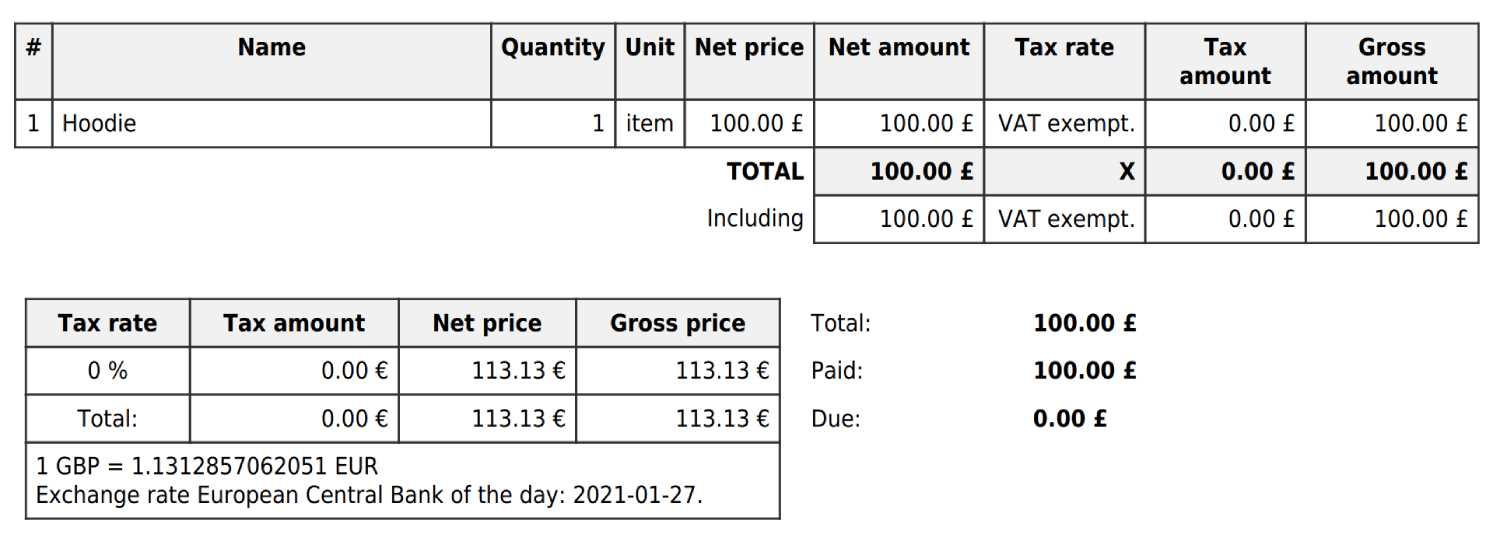
In international trade, businesses often encounter the need to adjust how they calculate and report taxes. Specific mechanisms are in place to ensure proper tax application across borders, especially when it comes to cross-border sales or services. These systems aim to simplify the process of tax compliance and avoid double taxation on goods and services.
One of the most important methods of managing such transactions involves shifting the responsibility for tax reporting from the seller to the buyer. This approach helps streamline operations for businesses and ensures that the tax system remains fair and efficient. By utilizing specific forms and formats, businesses can accurately reflect these arrangements in their financial records.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects of structuring and utilizing these specialized forms. Understanding how to correctly create and manage these documents will help you stay compliant with tax regulations while improving your business operations. Accuracy and clarity are crucial when preparing such records, ensuring that all parties involved are aware of their tax responsibilities.
What is a Reverse Charge Invoice
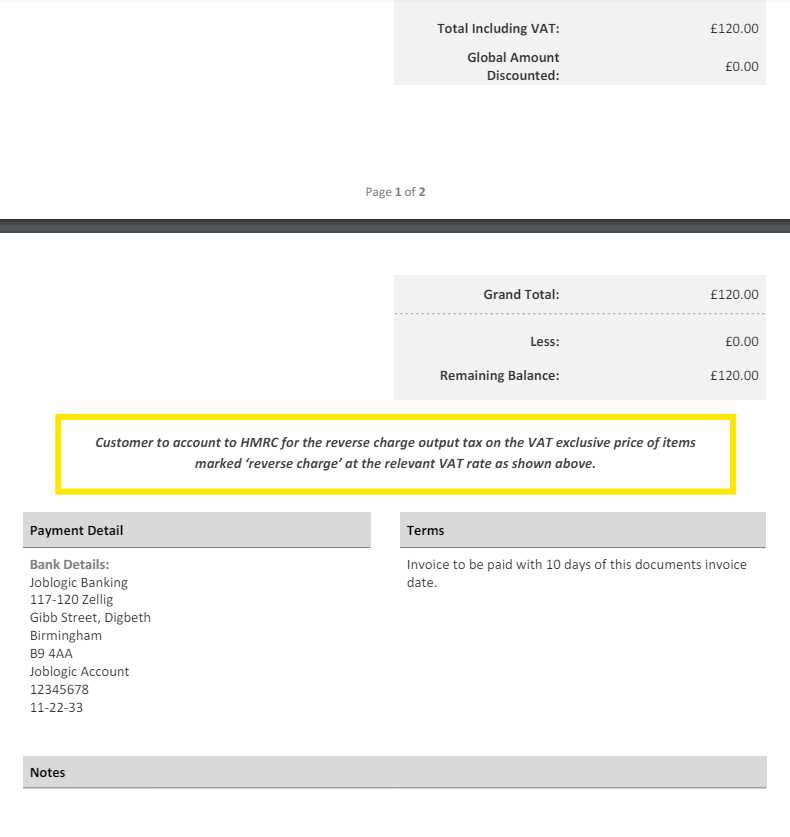
In certain business transactions, especially those involving cross-border trade, there is a unique method for handling tax responsibilities. This approach shifts the burden of calculating and reporting taxes from the seller to the buyer, ensuring compliance with international tax regulations. It is commonly used in situations where the buyer is more familiar with the tax laws of their own country and can handle the required documentation more efficiently.
The core idea behind this mechanism is that the buyer, rather than the seller, is responsible for paying the applicable tax on the goods or services provided. This simplifies the process for sellers who do not need to worry about calculating the tax themselves, and instead can focus on delivering their goods or services. However, it also places a responsibility on the buyer to ensure that the tax is paid correctly.
To manage this process, a special document format is used to outline the transaction and tax details. These documents clearly specify that the buyer will handle the tax reporting, and they provide the necessary information to complete the transaction. A properly structured document helps both parties comply with the law and avoids confusion during audits or tax reporting processes. Accuracy in these records is essential for both buyers and sellers, ensuring transparency and legal compliance.
Understanding VAT Reverse Charge Mechanism
In the context of international trade, businesses need to manage tax obligations effectively, especially when goods or services are exchanged across borders. One system designed to simplify tax collection is the shifting of tax responsibility from the seller to the buyer. This mechanism is particularly important in the European Union and other regions where cross-border transactions often involve complex tax rules. By using this method, businesses ensure that the correct tax amount is reported and paid, without causing confusion or delays in the transaction process.
How It Works
The primary purpose of this system is to streamline VAT reporting and prevent double taxation. In a standard transaction, the seller is responsible for charging VAT and remitting it to the tax authorities. However, under this system, the buyer takes on the responsibility for paying the tax, and the seller only needs to issue a document that clearly indicates this arrangement. The buyer then reports and pays the tax directly to the relevant authorities in their country.
Benefits for Businesses
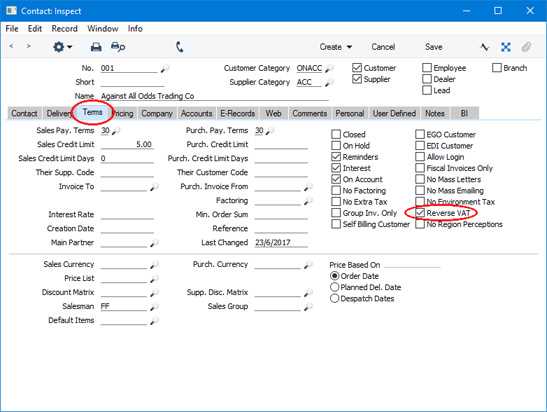
This method simplifies the tax process for businesses, especially when dealing with international sales. It helps reduce the administrative burden on sellers who no longer have to calculate, collect, and remit taxes for foreign customers. The system also ensures that the correct tax rate is applied according to the buyer’s location and tax laws, reducing the risk of errors in tax reporting.
| Party Responsible | Seller’s Role | Buyer’s Role |
|---|---|---|
| VAT Payment | None | Responsible for paying VAT |
| Tax Reporting | Issue a clear document indicating the transaction | Report and remit VAT to tax authorities |
| Tax Rate | None (depends on buyer’s location) | Determined by buyer’s country laws |
Key Elements of Reverse Charge Invoices
When managing transactions under the special VAT mechanism, it is essential to ensure that all relevant details are clearly outlined in the document. This helps both the seller and buyer understand their responsibilities and ensures compliance with tax regulations. Key elements should be present to avoid any confusion or errors during audits or financial reporting. These elements provide transparency and make the transaction process smoother for all parties involved.
Essential Information to Include
The document should contain several critical pieces of information that highlight the shift in tax responsibility. Below are the necessary details that must be included:
- Buyer and Seller Details: Full names, addresses, and VAT identification numbers of both parties.
- Transaction Date: The date the goods or services were delivered or completed.
- Detailed Description of Goods/Services: A clear description of what is being sold, including quantity and price.
- VAT Indication: A statement clearly indicating that the buyer is responsible for VAT payment.
- Invoice Number: A unique reference number for tracking purposes.
Additional Information to Include
Besides the essential details, there are other pieces of information that can help clarify the transaction further:
- Tax Rates: Specify the applicable VAT rates based on the buyer’s location or the product category.
- Exemption or Special Conditions: Any exemptions or special conditions that apply to the transaction should be clearly stated.
- Currency: Ensure the transaction currency is clearly indicated, especially in cross-border dealings.
Why Use a Reverse Charge Invoice
In international business transactions, handling VAT responsibilities can become complex, especially when goods or services cross borders. By shifting the responsibility for tax payment, businesses can simplify the process and ensure they stay compliant with tax regulations. This method benefits both sellers and buyers by reducing the administrative burden and helping avoid double taxation on cross-border transactions.
Advantages for Sellers
For sellers, utilizing this system offers several key benefits that streamline operations and ensure tax compliance. Below are the main advantages:
- Simplified Tax Reporting: Sellers don’t need to calculate and remit VAT, which can be especially complicated in cross-border trade.
- Reduced Risk of Errors: Since the buyer handles the VAT payment, the risk of incorrect tax calculations is minimized for the seller.
- Faster Transactions: By removing VAT from the seller’s responsibility, the transaction process becomes quicker and more efficient.
Benefits for Buyers
Buyers also gain advantages by taking on the tax responsibility, ensuring that the tax process is transparent and compliant with their local laws. The key benefits include:
- Control Over Tax Payments: Buyers are able to manage their VAT payments directly with their local authorities, ensuring the correct tax rate is applied.
- Avoidance of Double Taxation: This mechanism helps prevent VAT from being paid twice on the same transaction.
- Streamlined Tax Reporting: Buyers benefit from clearer tax records, making it easier to report and pay taxes on their end.
When to Issue a Reverse Charge Invoice
In specific business transactions, the responsibility for VAT payment is transferred from the seller to the buyer. This arrangement is commonly used in cross-border sales and services, particularly within regions that have complex VAT regulations, such as the European Union. Understanding when to implement this system ensures that both the buyer and seller meet their legal obligations while simplifying the overall tax process.
Conditions for Using This System
There are several scenarios in which this method should be applied. Below are the key situations where it is appropriate to transfer the tax responsibility to the buyer:
- Cross-Border Transactions: When goods or services are sold between different countries, especially within regions with harmonized VAT laws.
- Business-to-Business Sales: Typically, this system applies to transactions between two VAT-registered businesses, as they are more familiar with VAT reporting requirements.
- Specific Goods or Services: Certain goods or services, such as digital services or construction work, may require this tax shift according to local regulations.
When Not to Use This System
There are also situations where this mechanism should not be applied. In these cases, the seller remains responsible for VAT calculations and reporting:
- Domestic Transactions: When both the buyer and seller are based in the same country and subject to the same VAT rules.
- Sales to Non-VAT Registered Buyers: If the buyer is not VAT-registered, they will not be able to handle the VAT payment on their own.
- Exempted Goods or Services: Certain goods or services, such as those exempt from VAT or outside the scope of VAT, should not follow this process.
How to Format a Reverse Charge Invoice
Creating a document that reflects the shift in tax responsibility requires attention to detail to ensure clarity and compliance with tax regulations. The correct structure helps both the buyer and the seller understand their roles in the transaction, particularly when it comes to handling VAT. A well-organized document not only simplifies the process but also prevents errors in tax reporting.
Essential Information to Include
There are several critical components that must be clearly outlined in the document. These elements ensure that both parties are aware of the tax responsibilities and that the transaction is documented correctly:
- Transaction Details: Include the date of the transaction, a unique reference number, and a description of the goods or services provided.
- Seller and Buyer Information: Clearly state the names, addresses, and VAT identification numbers of both parties involved.
- Tax Statement: Indicate that the buyer is responsible for paying the VAT, usually with a clear statement such as “VAT is accounted for by the buyer.”
- Amount and Currency: Provide the total amount for the transaction, along with the applicable currency.
Formatting Tips for Clarity
To ensure the document is easy to read and understand, consider the following formatting tips:
- Clear Layout: Use headings and bullet points to break up the content into easily digestible sections.
- VAT Details: List the applicable VAT rates, and if possible, include the buyer’s VAT number and the seller’s VAT number for reference.
- Legibility: Ensure the font size is large enough for easy reading, and use a simple, professional design to keep the focus on the important information.
Common Mistakes in Reverse Charge Invoices
When handling transactions under the special VAT mechanism, there are several common errors that can complicate the process for both the seller and buyer. These mistakes often arise due to misunderstanding the requirements or failing to include crucial details in the document. Ensuring that all necessary information is correctly presented can help prevent issues with tax authorities and ensure smooth business operations.
One of the most frequent mistakes is the failure to include a clear statement about the transfer of VAT responsibility. Without this explicit mention, it may not be evident to the buyer that they are responsible for paying the tax, leading to confusion or potential non-compliance. Additionally, errors in the VAT rates applied or failure to include the appropriate VAT identification numbers can result in discrepancies and delays in tax reporting.
Another common issue is not properly documenting the transaction details. Omitting key information such as the buyer’s and seller’s VAT numbers, the nature of the goods or services, or the total amount involved can cause the document to be rejected during audits or tax reviews. It’s crucial to ensure that all fields are filled out accurately and completely to avoid these complications.
Legal Requirements for Reverse Charge Invoices
When using the special VAT mechanism, it is essential to ensure that all legal obligations are met. There are specific regulations that govern how these documents should be formatted, what information must be included, and how tax responsibilities should be transferred between the buyer and seller. Adhering to these legal requirements helps avoid penalties, audits, or complications with tax authorities.
Mandatory Information
To comply with legal standards, certain details must always be included in the document. These include:
- VAT Identification Numbers: Both the seller’s and the buyer’s VAT numbers should be clearly listed to confirm that both parties are registered for VAT.
- Clear Statement of Tax Liability: The document should explicitly indicate that the buyer is responsible for the VAT payment. A common phrase used is “VAT accounted for by the buyer.”
- Transaction Details: Information about the goods or services, including quantity, price, and total amount, must be accurately reflected in the document.
Compliance with Local and International Tax Laws
It is important to understand that the legal requirements for such documents can vary depending on the country or r
Reverse Charge Invoices in Different Countries
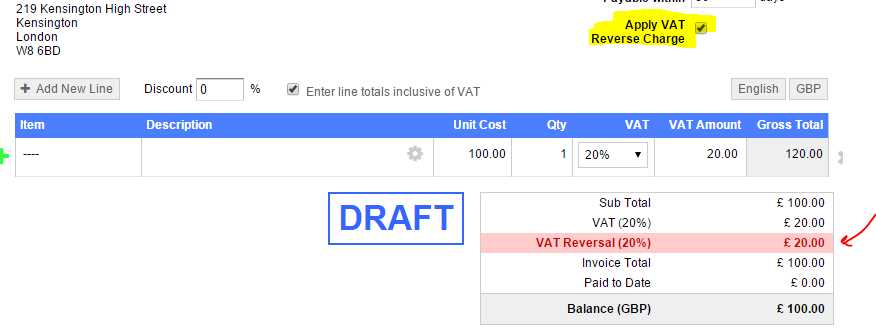
The application of the VAT mechanism that shifts tax responsibility can vary widely between countries. Different nations have their own specific rules and regulations regarding when and how this system should be implemented. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses that operate across borders, as it helps ensure compliance with local tax laws and avoids penalties.
European Union Regulations
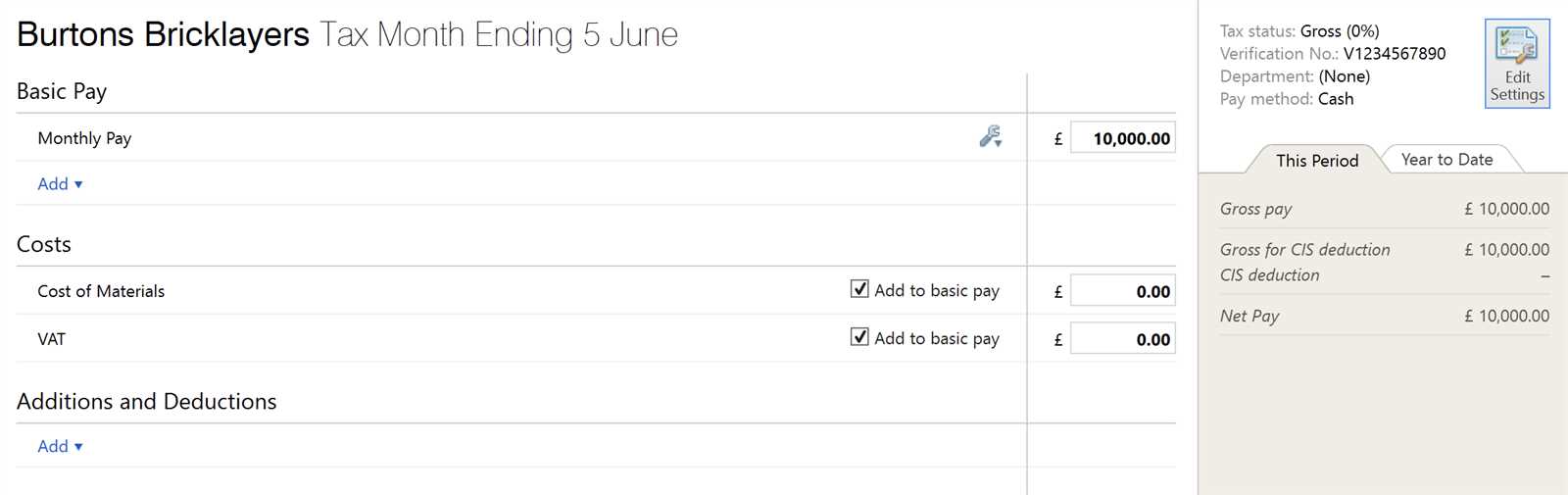
In the European Union, this tax shift is commonly used in cross-border transactions between businesses. The EU has harmonized many VAT rules, which means the reverse VAT mechanism applies in several situations, such as for the sale of goods between EU member states or when certain services are provided across borders. However, each member state may have additional rules or exemptions that apply to specific industries or transactions. Businesses within the EU must ensure they are familiar with both EU-wide and local regulations when handling these types of transactions.
Non-EU Countries
Outside the EU, the application of this system varies significantly. In countries like the United States, VAT is not used, so a different set of tax rules applies to cross-border transactions. However, countries like Australia and Canada do have similar mechanisms for handling goods and services tax (GST) or sales tax. Understanding the specific tax framework in each country is vital for businesses involved in international trade to ensure proper tax handling and reporting.
Impact of Reverse Charge on Businesses
The implementation of the mechanism where the tax responsibility is shifted can have a significant impact on businesses, particularly in terms of cash flow, tax reporting, and compliance. While this system can simplify certain aspects of tax management for sellers, it can also introduce complexities that need to be carefully managed to avoid financial or legal issues. Understanding the effects of this process is crucial for businesses that regularly engage in cross-border transactions or operate in industries where this mechanism is frequently applied.
Cash Flow and Payment Timing
One of the most notable impacts of this tax shift is on cash flow. Since the buyer is responsible for paying the VAT, the seller is relieved from collecting this tax. However, this can lead to delays in payment processing, as the seller may not receive the full amount upfront. As a result, businesses may need to adjust their payment terms or financing strategies to account for this change in cash flow.
Tax Compliance and Reporting
For businesses, staying compliant with tax regulations becomes even more critical when using this system. There is an increased need for accurate documentation and reporting, as failing to correctly apply the tax shift or misreporting tax liabilities can result in fines or audits. Companies must ensure that both parties involved in the transaction clearly understand their tax obligations, and this often requires additional administrative effort to track and report these details accurately.
Reverse Charge Invoices and International Trade
The tax mechanism that shifts the responsibility for VAT can significantly impact international trade. This system is often used in cross-border transactions to simplify the tax process, particularly when goods or services move between businesses in different countries. Understanding how this system operates in the context of global trade is essential for companies that engage in international transactions, as it ensures compliance with local tax laws while optimizing the flow of goods and services.
Benefits for Cross-Border Transactions
One of the key advantages of using this system in international trade is the reduction of administrative burdens for exporters. Since the responsibility for paying VAT falls on the buyer rather than the seller, businesses can avoid the need to register for VAT in multiple countries. This simplifies the export process, lowers the risk of errors, and ensures that the correct tax is applied at the point of sale.
Challenges in Global Commerce
While the tax shift mechanism offers benefits, it also introduces challenges in global commerce. Businesses must stay updated on the varying rules and regulations for tax responsibility in different countries. This can lead to confusion or mistakes, especially when trading with countries that have different VAT or sales tax structures. Furthermore, ensuring that both the buyer and seller clearly understand their obligations is crucial to avoid disputes or penalties.
Examples of Reverse Charge Invoices
Understanding how the tax responsibility shift works in practice is crucial for businesses. This mechanism is applied in various industries and countries, and recognizing common scenarios can help ensure that the proper procedures are followed. Below are some examples where this system is typically used, providing a clear picture of how the tax obligations are transferred in different situations.
Example 1: Cross-Border Goods Supply within the EU
In a transaction between two businesses located in different EU countries, the seller is not required to collect VAT. Instead, the buyer is responsible for calculating and remitting the tax. For instance, a company in Germany sells electronics to a business in France. The German supplier does not apply VAT to the sale, but the French business must account for VAT under the local rules and rates.
Example 2: Construction Services
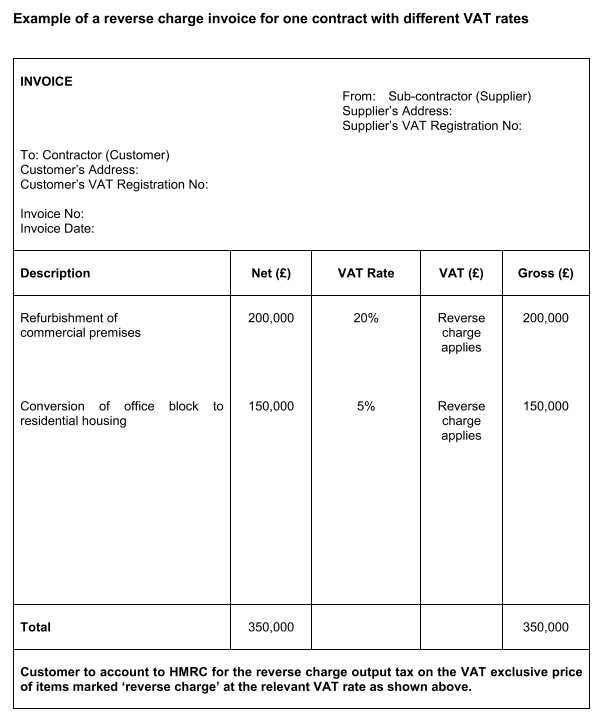
Another common example occurs in the construction industry, particularly in cases involving large projects. A subcontractor providing services to a main contractor may use this mechanism, depending on the local VAT laws. For example, a subcontractor providing construction services in the UK to a contractor will not charge VAT on the services rendered. Instead, the main contractor will account for VAT on the services received.
In both of these examples, the shift of tax responsibility simplifies the collection process for the seller and ensures that the buyer is accountable for the proper tax filings and payments. This process reduces the risk of tax evasion and streamlines VAT reporting, especially in cross-border transactions.
How Reverse Charge Affects VAT Filing
The shift in tax responsibility has a direct impact on how businesses file their VAT returns. When the buyer is responsible for accounting for the VAT, rather than the seller, it changes the way transactions are reported and the taxes are calculated. Understanding these effects is essential for accurate tax filings and compliance with local regulations.
Implications for Businesses
For businesses that engage in transactions where the responsibility for VAT is transferred, several changes in VAT filing need to be considered:
- Buyer’s Responsibility: The buyer must report the VAT on their VAT return as if they had paid it to the supplier. This often results in the buyer claiming both output tax and input tax, which can lead to a net-zero effect if the business is eligible to reclaim VAT.
- Seller’s Simplicity: The seller does not need to collect VAT or report it on their return, simplifying their filings. However, they still need to ensure the correct documentation and terms are provided to the buyer to validate the application of the mechanism.
- Compliance Checks: Both parties involved must ensure the tax shift is applied correctly to avoid penalties. This involves maintaining accurate records and ensuring that the correct codes and procedures are used in the tax filings.
Filing Process Considerations
Businesses need to account for specific details when filing VA
Reverse Charge Invoice Template Benefits
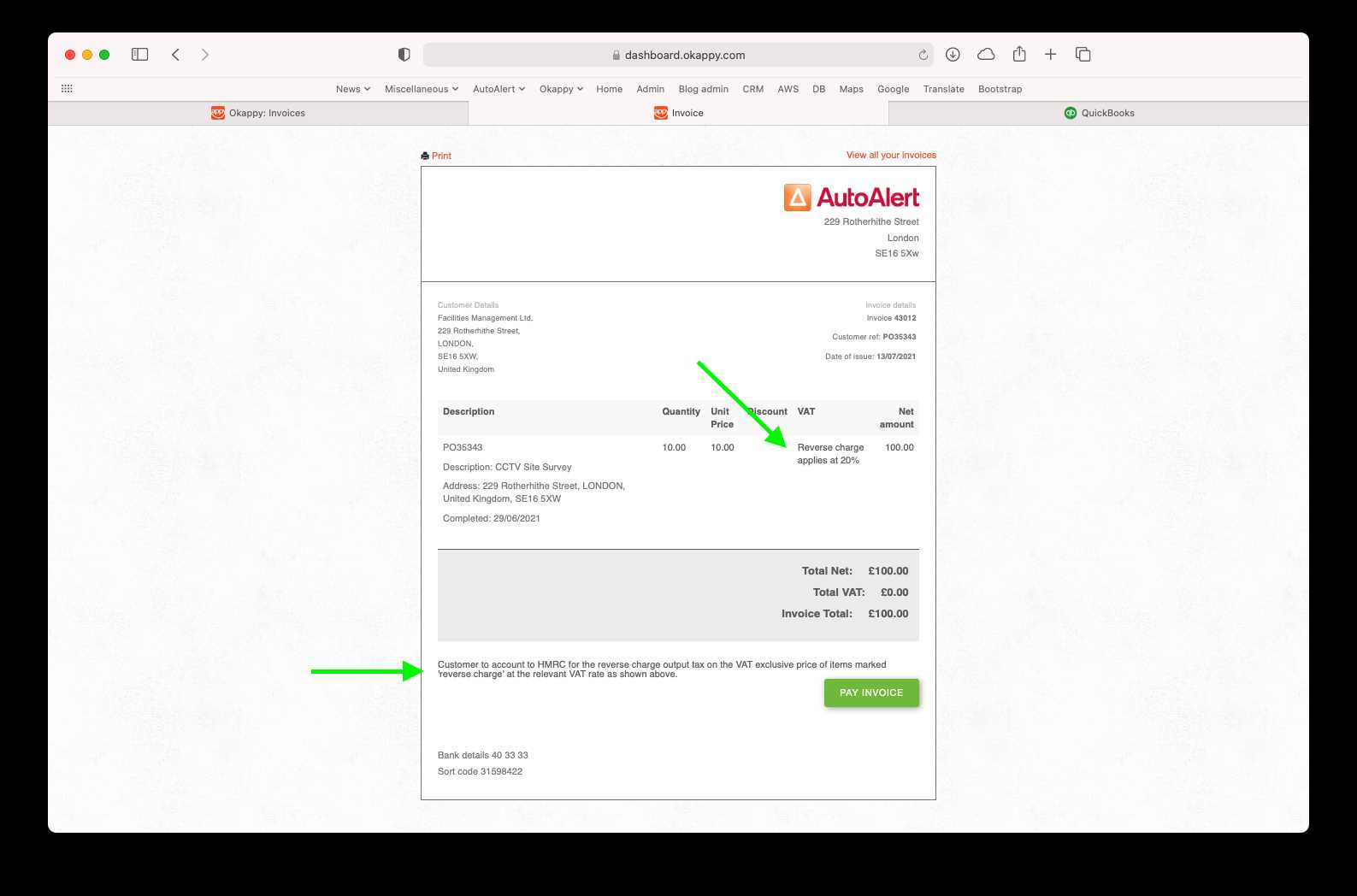
The application of this tax mechanism can significantly streamline business processes, offering numerous advantages for both suppliers and buyers. Utilizing the appropriate documentation format ensures that businesses remain compliant, simplifies administrative tasks, and helps avoid common mistakes. Below are some of the key benefits of using this approach in transactions.
Benefits for Businesses
- Efficiency in Tax Reporting: By transferring the responsibility for VAT, businesses can simplify their tax reporting process. Buyers can directly handle the tax filings, avoiding the need for suppliers to manage complex VAT collection on behalf of multiple customers.
- Reduced Risk of Tax Evasion: This system reduces the possibility of VAT fraud, as the tax is directly accounted for by the buyer, ensuring that the tax is paid and reported properly.
- Streamlined Transactions: With the tax responsibility shift, suppliers can focus on the sale without worrying about VAT collection. This can speed up the sales process, particularly in cross-border transactions.
- Improved Cash Flow: In cases where the buyer is responsible for VAT payments, the supplier may not face delays in receiving payments due to VAT processing. This can positively affect cash flow and reduce administrative burdens.
Benefits for Compliance
- Clear Documentation: The use of a standardized approach ensures that both parties understand their roles and obligations. This reduces confusion and ensures that each transaction is properly documented for tax purposes.
- Minimized Errors: Having a clear system in place with appropriate documentation reduces the risk of making errors when filing VAT returns. The buyer and seller both know exactly what information needs to be reported.
Ultimately, using the correct approach to document these transactions ensures smooth operations and reduces the complexity involved in tax reporting and payments. By leveraging th
How to Create a Custom Template
Creating a customized document format tailored to specific business needs is essential for ensuring smooth operations. A well-designed layout makes it easier for businesses to comply with tax requirements and simplifies the transaction process. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you craft a document suited to your business requirements.
Step 1: Choose the Right Software
The first step in designing your own document layout is selecting the software that fits your needs. Depending on your preferences and business scale, you can use simple word processors, spreadsheet software, or dedicated accounting programs. Popular options include:
- Microsoft Word: For simple documents with basic customization options.
- Excel: For businesses that need detailed tables and calculation functions.
- Accounting Software: Platforms like QuickBooks or Xero often offer built-in document creation tools for tailored layouts.
Step 2: Organize the Information
Once you’ve chosen the right software, start organizing the essential information that should appear on your document. Some of the core elements you need to include are:
- Company Details: Name, address, and contact information of your business and client.
- Transaction Data: Clear breakdowns of the product or service provided, along with quantities and pricing.
- Tax Information: Ensure that the appropriate tax identifiers and VAT details are displayed, including how tax is handled in the transaction.
- Terms and Conditions: Any payment terms, including due dates, late fees, a
Software Tools for Reverse Charge Invoices
Using the right software tools is essential for businesses that need to handle complex tax systems, especially when specific rules apply to transactions. These tools can streamline the process, ensure compliance, and minimize errors, making the creation and management of relevant documents much easier. Here are some software options that help automate the process while ensuring accurate record-keeping.
Software Key Features Best For QuickBooks Automatic tax calculations, customizable templates, multi-currency support Small to medium businesses with basic accounting needs Xero Online accounting with VAT handling, easy-to-use invoicing tools, reporting features Businesses looking for comprehensive accounting solutions with tax features FreshBooks Customizable document creation, expense tracking, automatic tax rates Freelancers and small businesses needing invoicing and accounting integration Zoho Books Customizable tax settings, multi-user access, easy integration with other Zoho apps Small businesses and startups looking for scalable accounting tools Sage Business CloudTips for Managing Reverse Charge Invoices 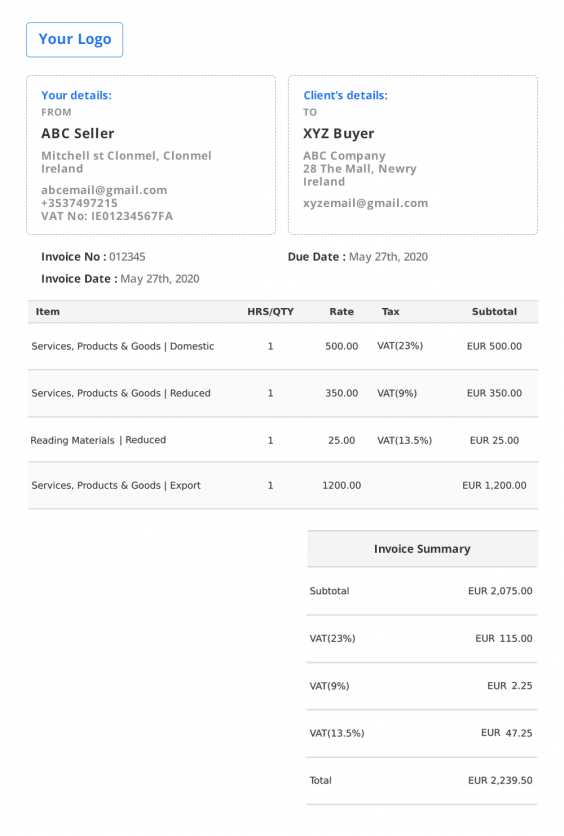
Managing transactions that involve shifting the responsibility for tax payment to the buyer can be complex. To ensure smooth processing and avoid errors, it’s important to stay organized and understand the specific requirements for each case. Below are some practical tips that will help businesses manage these types of transactions effectively and stay compliant with tax regulations.
1. Keep Accurate Records
Always maintain detailed records of all transactions where the tax responsibility is shifted. This includes keeping track of the goods or services sold, the buyer’s information, and any relevant tax rates. Proper documentation is crucial for tax reporting and for handling any potential audits.
2. Understand the Tax Laws
Each country may have different rules regarding these types of transactions. Stay informed about the specific tax regulations in your jurisdiction to ensure compliance. This knowledge will help avoid costly mistakes and ensure you’re following the correct procedures.
3. Use Automated Tools
Utilize accounting software or tools that can automatically calculate and apply the correct tax rates. These tools can simplify the process, reduce errors, and save time. Many programs also have built-in features that ensure tax requirements are met based on location and transaction type.
4. Communicate with Buyers
Clearly communicate with your customers about their responsibilities regarding tax payments. Make sure they are aware of the transaction details, especially when the tax is their responsibility. This transparency will help avoid confusion and ensure smoother transactions.
5. Regularly Review Tax Rates
Tax rates can change over time, so it’s important to review them regularly. Keep track of any updates to tax laws that may impact your transactions. Adjust your processes accordingly to ensure compliance and avoid